Polygons are closed two-dimensional shapes bounded by line segments. The segments meet in pairs at corners called vertices. A polygon is irregular if not all its sides are equal in length. The figure below shows examples of irregular polygons:
-
Implement a class IrregularPolygon that contains an array list of Point2D.Double objects.
-
The Point2D.Double class defines a point specified in double precision representing a location in (x, y) coordinate space. For example, Point2D.Double(2.5, 3.1) constructs and initializes a point at coordinates (2.5, 3.1).
- Use the following declarations as a starting point for your lab work.
import java.awt.geom.*; // for Point2D.Double
import java.util.ArrayList; // for ArrayList
import gpdraw.*; // for DrawingTool
public class IrregularPolygon{
private ArrayList <Point2D.Double> myPolygon;
// constructors
public IrregularPolygon() { }
// public methods
public void add(Point2D.Double aPoint) { }
public void draw() { }
public double perimeter() { }
public double area() { }
}
-
The program should use the Drawing Tool to draw the polygon by joining adjacent points with a line segment, and then closing it up by joining the end and start points.
- Write methods that compute the perimeter and the area of a polygon. To compute the perimeter, compute the distance between adjacent points, and total up the distances. The area of a polygon with corners
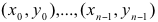 is the absolute value of:
is the absolute value of:
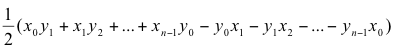
Note: add n products, then subtract n products, then divide by 2. The result will be negative or positive depending on the order in which the products are taken, i.e., which products are subtracted and which are added.
- As a test case, the parallelogram formed by the following coordinates has a perimeter of 174.1 units and an area of 1700 square units: (20, 10), (70, 20), (50, 50), (0, 40).


