-
Your instructor will provide you with a text file, (numbers.txt), containing a large (N <= 1000) number of integers. The integers range in value from 0 to 100. The text file has been created with one value on each line. Due to the potential for the sum of the numbers to be very large, you should use a long integer in your calculation to find the average.
-
The number of integers in the file is unknown.
-
Your program must find the average, standard deviation, and mode of the list of numbers. The mode is defined as the value(s) present with the highest frequency. Calculating the standard deviation consists of the following steps:
- Find the average of the list of numbers.
- Determine the difference of each number from the average, and square each difference. Sum all the differences.
- Divide this sum by (the number of values - 1).
- Take the square root of the above division result from step c.
-
Example, given this list of numbers: 7 4 5 9 10
- The average = 7
- Sum of square of differences:
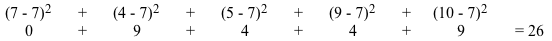
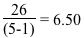
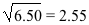
-
For a normal distribution, 68.3% of the data will lie within one standard deviation of the average, while 95.4% will lie within two standard deviations.
-
Your program should print out the average, standard deviation, and mode of the data in numbers.txt.
Format the real numbers to print with 2 decimal places.
-
Your program must utilize proper modular design and parameter passing.
-
Turn in your source code and run output.


